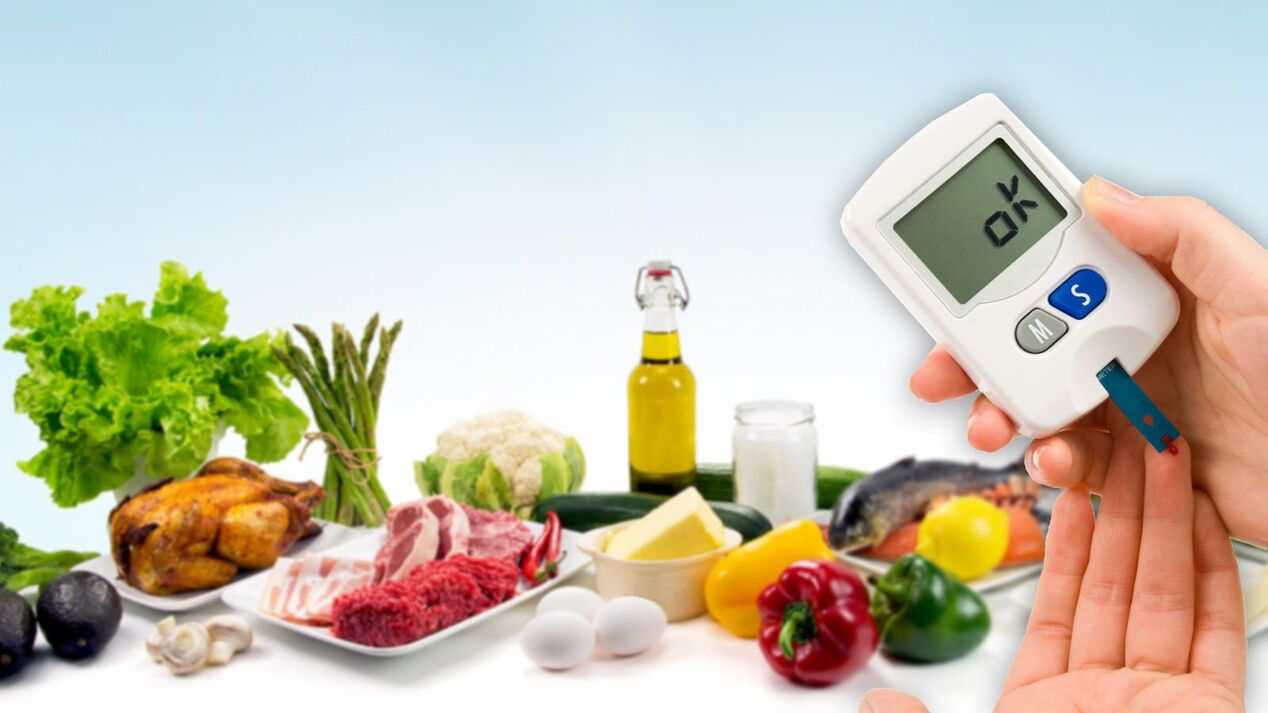
Etiology and pathogenesis
- overweight;
- Injury – physical and mental;
- viral diseases causing complications;
- genetic aggravation;
- Autoimmune diseases.
- general weakness;
- lose weight;
- Increased urine output and frequent urination;
- Wounds heal slowly;
- Decreased libido;
- Itching of mucous membranes;
- hair and nail deterioration;
- Increased appetite and frequent thirst.
Classification of diseases and role of nutrition
- Type I diabetes is an autoimmune disease and a relatively rare disease. It is characterized by extremely low levels of insulin production; in some cases, patients' bodies do not produce this hormone at all. Patients are forced to take regular injections, which is why the term "insulin dependence" is also used. A diet designed to lower blood sugar levels can help improve health and avoid the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Type II diabetes occurs in 90% of cases. It usually occurs in people who are overweight and live a sedentary lifestyle, who do not pay attention to their diet and consume large amounts of foods that increase blood sugar levels (flour, potatoes, sweets). The dietary structure should gradually return the weight to normal. Moderate physical activity is recommended for such patients.
- Gestational diabetes is a condition that can occur in pregnant women, especially those with severe intoxication during the second trimester. The diet for gestational diabetes should include adequate amounts of dietary supplements and strict weight control. In most cases, health returns to normal after pregnancy is over, but there is a risk of developing type 2 diabetes. To avoid this, you should follow the recommended diet after delivery.
diabetes diet type
Types of nutrition plans
- Protein diets are designed to suppress appetite by providing the body with large amounts of protein, thereby stimulating the production of bioactive substances. Proteins of plant and animal origin are introduced into the diet in equal proportions. Red meat is banned; replace it with fish, lean poultry, dairy products, and protein-rich beans and grains.
- A low-carbohydrate diet for diabetes based on vegetables and fruits containing complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates were banned and protein intake was limited. This nutritional system is considered strict and is used when blood sugar levels are significantly elevated (3 times or more).
- Low-carb diets are milder and suitable for people with type I and type II diabetes.
- A buckwheat diet normalizes metabolic processes and replenishes the body with vitamins, macro and trace elements.
- The basis of a preventive diet is the replacement of red meat with protein-rich lean meat, the use of appropriate cooking methods and the intake of fiber.
- The Bernstein Diet is good for type 2 diabetes and prevention. This is not just a menu, but a comprehensive approach to organizing a balanced diet that can be taught even to young children.
carb counting
- 1 tbsp. lake sugar or honey;
- 150ml juice;
- 130 g oranges;
- 60 g banana;
- 100 g melon;
- Porridge – 2. 5 tbsp. lake-grown cereals;
- Milk and fermented milk drinks – 250 ml;
- 20 g dried fruit.
type 1 diabetes diet
- Part of the patient's nutrition: 5-6 meals a day.
- The maximum daily caloric content is 2000 kcal.
- Carbohydrates for breakfast, lunch and dinner.
- Eat at least some snacks in the evening.
- No fast carbs.
- Say no to sugar and replace it with safe analogues (stevia, synthetic sweeteners).
- Long-acting insulin preparations are given before meals, and short-acting insulin preparations are given after meals.
- The maximum intake of XE per meal is 8.
- Natural products are preferred.
A weekly diet for an overweight insulin-dependent person
first day
- A piece of bread, porridge, soft cheese, tea.
- Oranges, pistachios.
- Borscht, salad, cabbage stew, schnitzel, gavage.
- Rose hips, cheese, jelly.
- Steamed cauliflower, salad.
- A glass of milk.
the next day
- Steamed veal, tomatoes, cereal bread, tea.
- cheese, half a ripe pear.
- Chicken breast, pumpkin puree, salad.
- Grapefruit, kefir.
- Boiled fish and stewed cabbage.
- biscuit.
The third day
- Lavash, coffee, cabbage rolls.
- Strawberries, yogurt.
- Solid pasta, salads, steamed fish.
- Orange, candied fruit.
- Cheese Casserole.
- Kefir.
The fourth day
- Porridge, cheese, boiled eggs, tea.
- Toast bread with soft cheese and cook turkey.
- Vegetable puree soup, vegetable stew, bread.
- Tea and biscuits.
- Green beans with chicken breast and rosehips.
- bread.
fifth day
- Cheese and kefir.
- Pumpkin seeds, raisins.
- Potatoes, salad, preserves.
- Roasted pumpkin, rosehips.
- Salads, rye flour pancakes.
- Kefir.
The sixth day
- Eggs, lightly salted salmon, tea.
- Cheese, carrots.
- Borscht with sorrel, vegetarian cabbage rolls, grout.
- Kefir, bread.
- Chicken tenders, braised eggplant, and fresh green beans.
- biscuit.
Day 7
- Porridge with ham and tea.
- Tuna and vegetable salad, whole wheat bread.
- Cabbage soup, meat stew, bread.
- Cheese, plums.
- Squid schnitzel, candied fruit.
- milk.
type 2 diabetes diet
Daily diet for type 2 diabetes
first day
- Asparagus and quail egg omelette.
- Nut, apple and boiled squid salad.
- Beetroot soup, roasted eggplant.
- Avocado, cocoa.
- Salmon steak with sauce.
the next day
- Oatmeal, yogurt, apples.
- Smoothies.
- Roast meat (veal) and vegetables.
- Cheese Casserole.
- Green salad with avocado.
The third day
- Fried eggs with cheese, tomatoes and herbs.
- Steamed vegetables with hummus.
- Vegetable puree soup, chicken steak, fresh peas.
- Pears and almonds.
- Salmon with spinach and yogurt.
The fourth day
- Baked apples.
- Toast with leafy greens and tuna.
- Steak, salad greens, parmesan cheese.
- Fruit sorbet.
- Broccoli Casserole.
fifth day
- Oranges, soft cheese, cereal bread, fruit tea.
- Beet salad with nuts and butter.
- Steamed fish, rice, grapefruit.
- Berries with cream.
- Squid schnitzel, rose hips.
The sixth day
- Carrot and Tofu Soufflé.
- Roasted broccoli.
- Lent borscht, grilled chicken slices, leafy greens, oranges.
- Berry mousse.
- Fish served with steamed vegetable garnish.
Day 7
- Baked apples with raisins, oatmeal and nuts.
- Salad with vegetables and shrimp.
- Polenta, boiled fish, vegetables, kiwi.
- Strawberry Cream Cheese.
- Cucumber and herb salad, tea.
gestational diabetes diet
- Excludes flour, baked goods, any store-bought sweets, semolina porridge and any sugary products.
- BJU standard: 20|30|50%. You need to balance your diet based on these indicators.
- Include fruits, dairy products, and starchy foods in your diet.
- Strictly adhere to drinking habits. You need to consume 1. 8-2 liters of drinking water every day.
- Aim for 3 main meals and 2 snacks each day.
- Minimize coffee and tea intake (no more than 2 cups per day).
- Take a special vitamin complex as recommended by your doctor.
- Introduce herbs into the diet to reduce sugar: decoctions of linden flowers, blueberry leaves, clove buds, celery root.
Recommended menu for expectant mothers with high blood sugar
- Breakfast: porridge (oatmeal, millet, buckwheat), cereal bread, tea or dried fruit preserves.
- Second breakfast: toast with unsalted cheese and apples.
- Lunch: porridge, vegetable salad, stew (beef or chicken).
- Afternoon snack: cheese, crackers, oranges.
- Dinner: Vegetable side dish, boiled meat, juice, crackers or pita bread.
Diet for children with insulin-dependent diabetes
Diet for children with diabetes
- Candy, candies, baked goods, sweetened sodas are prohibited. Sugar should be completely eliminated from the diet.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits are allowed, but you need to be aware of exceptions. Children with diabetes should not eat bananas, dates, persimmons, raisins, grapes or figs.
- Six meals should be arranged and the children should be fed strictly according to the time. The deviation should not exceed 20 minutes. If you can't eat enough, you should give your baby some fruit, bread, or toast. Children who are dependent on insulin should never go hungry.
- Monitor your fructose consumption and use this metric as a basis when calculating your allowable amount of sweetener.
- A piece of dark chocolate can stop a hypoglycemic episode. It is recommended that an accompanying adult carry this product with him or her at all times.
- Diet is important. Daily standards are calculated by the treating endocrinologist based on the child's age and size.